Let’s dive deep into the fascinating world of Decentralized Identifiers!
We navigate our days with clicks, swipes, and taps, engaging in countless digital interactions. Convenient? To a point, aside from the frustration of repetitive form-filling. Secure? Far from it — each interaction leaves a digital footprint, exposing our private data to potential risks.
What’s the solution? Data protection laws? They lag behind reality. Awareness campaigns? Easily ignored as we trade privacy for convenience. Hopeless then? Not at all! Enter Decentralized Identifiers, or DIDs for short.
This technology revolutionizes our online experience, shifting from a free-for-all where private data is at risk, to a digital future grounded in data ownership, privacy, and security. As we explore the innovative tech at the foundation of Empeiria’s End-to-End Verifiable Data Infrastructure (EVDI), let’s spotlight DIDs, which enable a transformative leap from the era of email logins to a decentralized, passwordless world.

What are Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)?
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) are a unique form of identifiers that enable independent management of digital identities without reliance on centralized authorities.
Think of DIDs as unique digital ID cards for the internet, whether for people, devices, or any other. Instead of being controlled by a single authority (like a government or a company), DIDs are managed by the entities themselves. DID doesn’t hold any information itself, but acts as a reference point.
What are DIDs for?
Here’s what you need to know: DIDs enable people to own and control their digital identities without relying on centralized authorities.
How? They achieve this through decentralized technologies such as blockchain, which ensures that identity information is stored securely and can be accessed and verified without intermediaries and associated risks.
With DIDs, people can easily create unique digital identifiers that are cryptographically verifiable and tamper-proof (meaning that they cannot be forged or altered by malicious actors). This empowers people to confidently and securely prove their identity, whether to log into websites, securely and privately share data, make transactions, or access services.
Here are some examples of practical use cases of DIDs:
- Secure Logins: Simplify access to multiple services with a single, decentralized identity.
- Digital Signatures: Securely sign digital documents and transactions.
- Credential Verification: Verify educational certificates and professional licenses.
- Personal Data Management: Securely manage and share personal information(e.g., health records).
- Access Control: Grant secure access to buildings, events, and digital resources.
- Financial Transactions: Streamline KYC processes and enhance payment security.
- Supply Chain Management: Verify product authenticity and track products.
- Voting and Governance: Enable secure electronic voting and participation in DAOs.
- IoT Device Management: Authenticate and manage IoT devices.
DIDs support the principles of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), which emphasize the importance of people having full ownership and control over their data. This means that you can choose what data to share, who to share it with, and for how long, thus mitigating privacy risks and reducing the risk of data breaches.
In essence, DIDs represent a fundamental shift in how we manage our digital identities, placing people in charge of their data and empowering them with greater privacy, security, and control.
How to Create and Use a DID?
Creating a DID is a straightforward process that empowers you with control over your data. Follow these steps to get started:
- Install a Verifiable Data Wallet: Begin by downloading and installing a DID-compatible wallet, such as the Empe DID Wallet. These apps provide a secure environment to manage your DIDs and interact with various platforms.
- Create Your DID: Open the wallet app and follow the prompts to create a new DID. This typically involves generating a unique identifier and saving a recovery phrase. Ensure you store this recovery phrase securely, as it is essential for recovering your DID in case you lose access to your device.
- Link your DID to a Platform: To use your DID for logging into a platform, visit the platform and select the “Login with DID” option. This will initiate the process of linking your DID to the platform.
- Scan QR Code (if applicable): Some platforms may display a QR code as part of the login process. Use your DID wallet app to scan this QR code. This step securely shares your DID with the platform without exposing sensitive information.
- Authenticate Request: After scanning the QR code, you’ll receive a login request in your DID app. Authenticate this request using your preferred method, such as a PIN, password, or biometric verification.
Once authenticated, the platform will verify your DID and log you in. This seamless process ensures your identity is verified securely, without the need for traditional usernames, email addresses, and passwords.
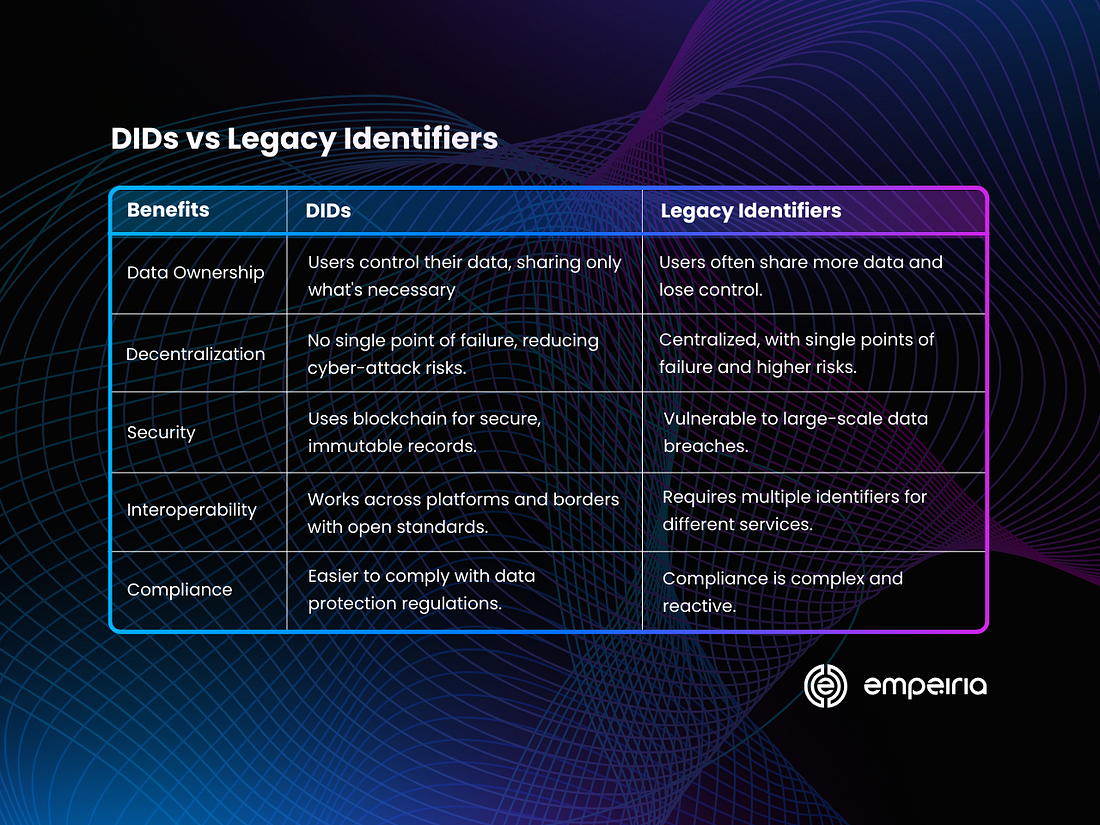
What makes DIDs better?
In our current digital interactions, we mostly rely on email addresses, passwords, and logins. You’re sure to have more than a few of those yourself. Or maybe you trade your privacy for convenience by sharing your private data with tech giants to “Log in with Facebook, Google, or Amazon”? Either way, there is a better way. Here’s what sets DIDs apart:
Data Ownership: With DIDs users have full control over their data, deciding what to share, with whom, and for how long. DIDs minimize exposure by allowing users to share only the necessary information required for a transaction.
Decentralization: DIDs reduce dependence on single entities for managing and verifying identities. This introduces resilience to single points of failure and cyber-attacks compared to centralized systems.
Security: DIDs mitigate risks of large-scale data breaches by avoiding centralized data repositories. Instead, DIDs utilize blockchain for secure, immutable records of identity transactions.
Interoperability: DIDs can be used across various platforms, organizations, and borders, eliminating the need for multiple identifiers. They employ open standards designed for compatibility across different systems and technologies.
Compliance: By protecting user data privacy, DIDs can streamline compliance with the ever-changing data protection regulations like GDPR
The Rise of DIDs
The concept of Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) began to solidify around 2017, fueled by growing anxieties around online privacy and the erosion of data security. This innovative approach to digital identity management stemmed from a collaborative effort by the tech community, particularly experts in decentralized systems and cryptography. Key players in this movement included:
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C): This international community of technology companies and organizations that first began exploring and potentially setting the groundwork for DID standards. Their work continues to ensure interoperability across different platforms and systems, paving the way for widespread adoption.
The Decentralized Identity Foundation (DIF): This non-profit organization brought together stakeholders from various sectors — including technology developers, academics, and policymakers — to foster collaboration and accelerate the development of DID technology.
The rise of DIDs represents a significant shift in the way we manage our digital identities. By placing control in people’s hands, DIDs can create a more secure and user-centric online environment.
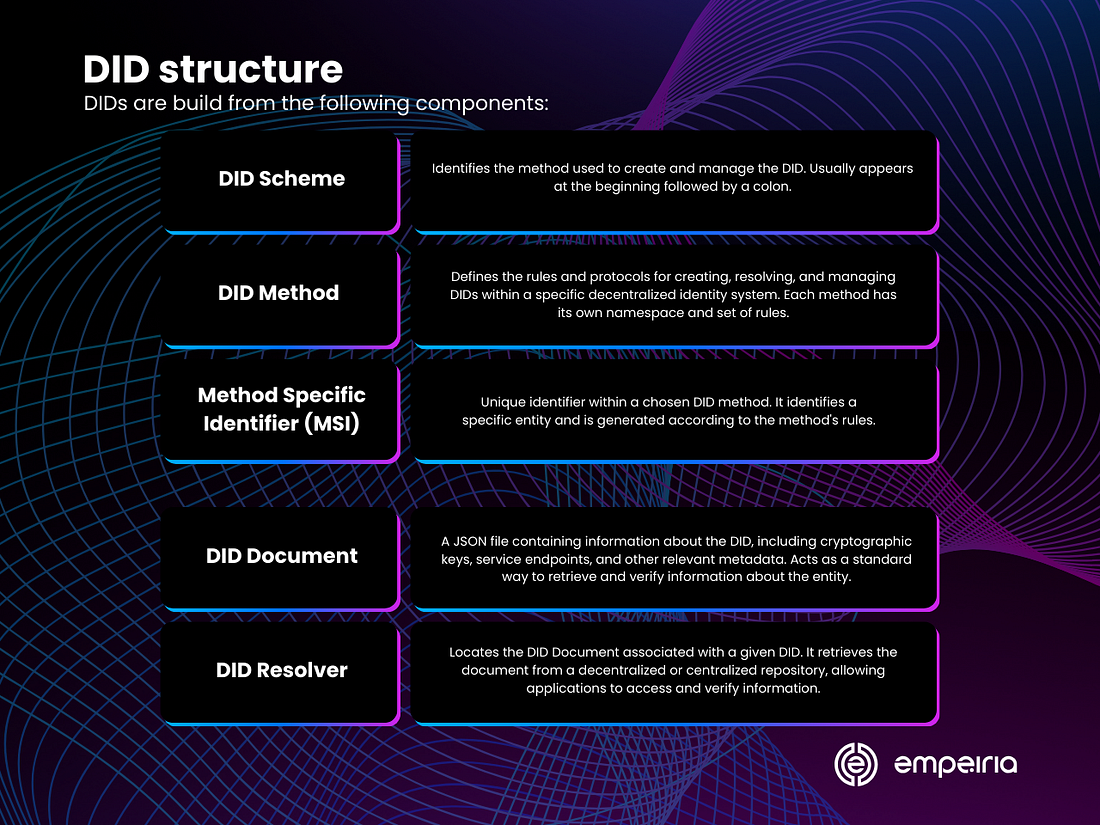
DID structure
DIDs are build from the following components:
DID Scheme: The DID scheme specifies the method or protocol used to create and manage the DID. It typically appears at the beginning of the DID and is followed by a colon. Examples of DID schemes include “did:ethr” for Ethereum-based DIDs and “did:web” for DIDs based on web technologies.
Method Specific Identifier (MSI): The Method Specific Identifier (MSI) is a unique identifier within the context of the chosen DID method. It’s the part of the DID that identifies a specific entity or subject. The MSI is generated according to the rules defined by the DID method and is unique within the scope of that method.
DID Document: The DID Document is a JSON file associated with a DID. It contains information about the DID, including cryptographic material, service endpoints, and other metadata related to the entity’s identity. The DID Document provides a standard way to retrieve and verify information about the entity represented by the DID.
DID Resolver: A DID Resolver is a component of a decentralized identity system responsible for resolving DIDs to their associated DID Documents. It retrieves the DID Document corresponding to a given DID from a decentralized or centralized repository, allowing applications to access and verify the information associated with the DID.
DID Method: A DID Method defines how DIDs are created, resolved, and managed within a specific decentralized identity system. It specifies the rules, algorithms, and protocols for generating DIDs, updating DID Documents, and performing other operations related to DIDs. Each DID method has its namespace and set of rules for creating and resolving DIDs.
Overall, the structure of DIDs encompasses the DID scheme, Method Specific Identifier (MSI), DID Documents, and associated components like the DID Resolver and DID Method. Together, these elements enable the creation, management, and utilization of decentralized identifiers for secure and interoperable digital identity solutions.
The role of blockchain in managing DIDs
Blockchain plays a crucial role in managing Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) by providing a tamper-proof and decentralized ledger to store and manage the associated DID documents and their changes. Here are several key aspects of how blockchain contributes to managing DIDs:
Decentralization and Trust: Blockchain technology allows DIDs to be managed in a decentralized manner, eliminating the need for central authorities to control identity information. Instead, DIDs and their associated metadata can be stored across a network of nodes, ensuring that no single entity controls the entire system. This decentralization enhances trust and resilience, as the integrity of the identity data is maintained by consensus among network participants.
Immutable Record of Changes: Blockchains provide an immutable record of all changes made to DID documents. Each update to a DID, such as adding or removing public keys or updating service endpoints, is recorded as a transaction on the blockchain. This transparent and tamper-evident history ensures that the integrity and authenticity of the identity data can be verified by any party with access to the blockchain.
Security and Privacy: By leveraging cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms, blockchain ensures the security and privacy of DID management. DIDs are associated with cryptographic keys, allowing entities to authenticate themselves and control access to their identity information. Additionally, blockchain enables selective disclosure of identity attributes, allowing users to share only the necessary information for a particular transaction while keeping the rest of their identity data private.
Interoperability: Blockchain-based DID management facilitates interoperability between various decentralized identity systems and applications. Since DIDs are globally unique and their associated metadata is stored on a decentralized ledger, they can be used across different platforms and services without being tied to a specific provider or ecosystem. This interoperability enables seamless integration of identity verification and authentication processes across domains and applications.
Resilience and Availability: Blockchains provide resilience and availability by distributing the storage and processing of identity data across a network of nodes. This distributed architecture ensures that even if some nodes in the network fail or become unavailable, the identity data remains accessible and intact. As a result, blockchain-based DID management systems are highly robust and resilient to failures or attacks.
Summary
As Empeiria continues to push boundaries, we envision sophisticated DID structures and integrating cutting-edge advancements for a secure, efficient, and scalable system. But through all this, one thing remains constant: the user. We prioritize user control and privacy with robust management mechanisms, all while ensuring a smooth experience for creating, updating, and verifying your DIDs.
With Empeiria DIDs, we’re building a future-proof digital identity landscape that empowers individuals and organizations to navigate the evolving digital world with confidence.
Follow Empeiria on Twitter/X, or LinkedIn for the latest news & updates. For inquiries or further information, contact Empeiria at [email protected].